Kicking off with Using Customer Data to Drive Decisions, this topic is all about how businesses can harness customer data to make smart moves and boost success. From analyzing different types of data to utilizing insights for key decisions, this discussion is a game-changer.
Importance of Customer Data: Using Customer Data To Drive Decisions
Customer data is like the secret sauce that fuels successful business operations in today’s competitive landscape. By leveraging customer data to drive decisions, companies can gain valuable insights into their target market, preferences, and behavior, ultimately leading to more informed strategies and enhanced customer experiences.
Influencing Business Strategies
Customer data plays a crucial role in shaping business strategies. For instance, analyzing purchase history data can help businesses identify popular products and trends, leading to more targeted marketing campaigns and product offerings. Additionally, customer feedback data can provide valuable insights into areas of improvement, allowing companies to refine their products and services to better meet customer needs.
Enhancing Customer Experiences
Utilizing customer data can also lead to enhanced customer experiences. By personalizing interactions based on customer preferences and behaviors, businesses can create tailored marketing messages, recommendations, and promotions that resonate with their target audience. This level of customization not only increases customer satisfaction but also fosters loyalty and repeat business.
Types of Customer Data

Customer data comes in various forms, each providing valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. It is essential for businesses to collect and analyze different types of customer data to make informed decisions and improve the overall customer experience.
Quantitative Customer Data
Quantitative customer data consists of numerical information that can be measured and analyzed. This type of data includes metrics such as purchase history, website visits, click-through rates, and customer demographics. Quantitative data provides concrete evidence of customer behavior and helps businesses identify trends and patterns.
- Number of purchases made by each customer
- Conversion rates for different marketing campaigns
- Customer lifetime value
- Frequency of website visits
Qualitative Customer Data
Qualitative customer data, on the other hand, provides more subjective insights into customer preferences and opinions. This type of data includes customer feedback, reviews, surveys, and social media interactions. Qualitative data helps businesses understand the “why” behind customer behavior and emotions.
- Customer feedback on products or services
- Reviews on review platforms or social media
- Responses to open-ended survey questions
- Comments on social media posts
Structured vs. Unstructured Customer Data, Using Customer Data to Drive Decisions
Structured customer data is organized and stored in a format that is easily searchable and analyzable. Examples include data stored in databases or spreadsheets. Unstructured customer data, on the other hand, is not organized in a predefined manner and includes text documents, emails, social media posts, and images. Both types of data are valuable for gaining insights into customer behavior, and businesses need to utilize tools and technologies to effectively analyze unstructured data.
Understanding the different types of customer data and how to leverage them can help businesses make data-driven decisions that drive growth and customer satisfaction.
Collecting Customer Data
In order to make informed decisions based on customer data, businesses must first collect the necessary information through various methods and tools.
Methods for Collecting Customer Data
- Surveys: Sending out surveys to customers to gather feedback and preferences.
- Website Analytics: Tracking customer behavior on websites to understand their interactions.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media platforms to gather insights on customer sentiment.
- Point of Sale Data: Collecting data from transactions to understand purchasing patterns.
Role of Technology in Gathering Customer Data
Technology plays a crucial role in efficiently collecting and analyzing customer data. Advanced tools and platforms are used to automate the process and gather data in real-time.
Examples of Tools and Platforms for Data Collection
- Google Analytics: Tracks website traffic and user behavior.
- SurveyMonkey: Helps create and distribute surveys to gather customer feedback.
- Social Mention: Monitors social media platforms for mentions and sentiment analysis.
- Retail Pro: Collects data from point of sale systems in retail stores.
Analyzing Customer Data
When it comes to analyzing customer data, it’s all about extracting valuable insights that can help businesses make informed decisions. By diving deep into the data, companies can uncover patterns, trends, and preferences that can guide marketing strategies, product development, and customer service efforts.
Process of Analyzing Customer Data
- Start by cleaning and organizing the data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Utilize data analysis tools like Excel, Tableau, or Google Analytics to crunch the numbers and identify key metrics.
- Look for correlations, outliers, and trends in the data to understand customer behavior and preferences.
- Use statistical models and algorithms to predict future customer actions and optimize business strategies.
Data Analysis Tools for Understanding Customer Behavior
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software to track interactions and engagement.
- Social media analytics tools to monitor sentiment and engagement on various platforms.
- Heatmaps and click tracking tools to analyze website visitor behavior and optimize user experience.
- A/B testing platforms to experiment with different strategies and measure their impact on customer behavior.
Importance of Data Visualization in Interpreting Customer Data
- Data visualization helps in presenting complex data in a visual format that is easy to understand and interpret.
- Charts, graphs, and dashboards can reveal trends, patterns, and outliers that may not be apparent in raw data.
- Visual representations of customer data can aid in making data-driven decisions and communicating insights effectively within the organization.
Utilizing Customer Data for Decision Making
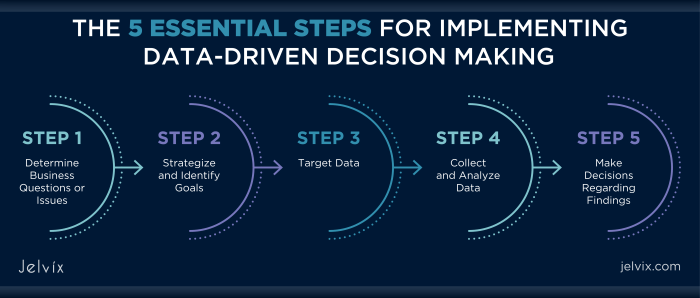
Customer data is a goldmine of information that can be used to drive informed business decisions. By analyzing this data, companies can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends, allowing them to tailor their strategies to meet the needs of their target audience.
Examples of Successful Decision-Making Based on Customer Data
- Netflix’s recommendation algorithm: Netflix uses customer data to analyze viewing habits and provide personalized recommendations, resulting in increased user engagement and retention.
- Amazon’s targeted marketing campaigns: Amazon leverages customer data to target specific demographics with personalized product recommendations, leading to higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Challenges Associated with Using Customer Data for Decision-Making
- Data privacy concerns: Companies must ensure compliance with data protection regulations and safeguard customer information to maintain trust and avoid potential legal consequences.
- Data accuracy and quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of customer data is crucial for making sound decisions. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to flawed conclusions and misguided strategies.
- Data integration and analysis: Consolidating data from various sources and analyzing it effectively can be challenging, requiring advanced analytics tools and expertise to extract actionable insights.